When you need an abdominal surgery, there are two main ways it can be done: laparoscopy (keyhole surgery, minimal invasive surgery) or open surgery (laparotomy). Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
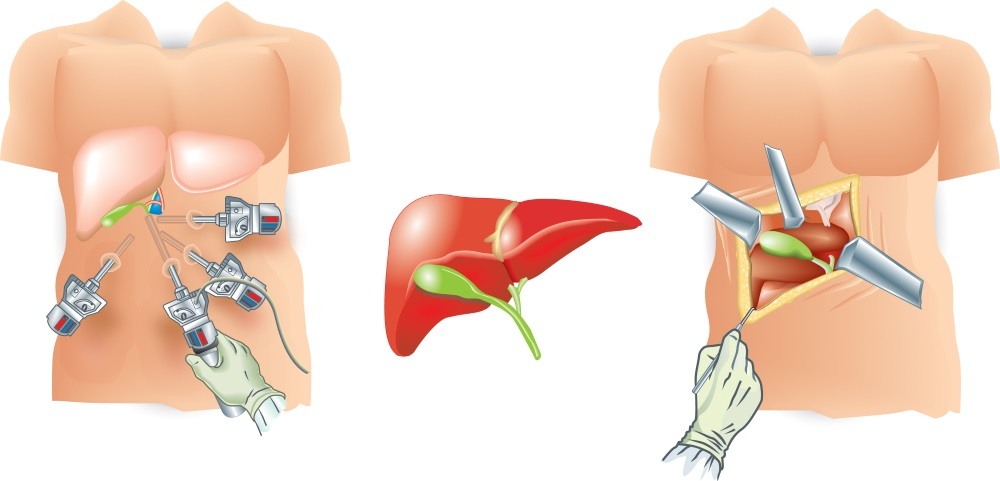
1. Laparoscopy (Minimally Invasive Surgery)
Laparoscopy is a technique where the surgeon makes small incisions (usually 0.5 to 1 cm) and inserts a tiny camera and special instruments to perform the surgery inside your body.
✅ Pros:
- Less pain after surgery: pain is often controlled with level 1 painkillers such as paracetamol. You may occasionally complain of shoulder pain. This is related to the removal of CO2 that helped inflate your abdomen for surgery. This pain will disappear quickly and is not considered serious.
- Faster recovery (you may go home sooner): you can often go home the same day as surgery depending on your doctors’ advice (surgeon and anesthesiologist). Faster recovery with laparoscopy means a shorter hospital stay, reducing exposure to hospital-acquired infections. Laparoscopy has a lower risk of complications, leading to a smoother recovery.
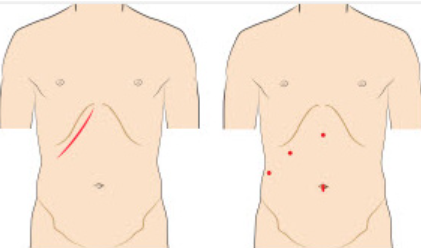
- Smaller scars (better cosmetic result): you have three or four small scars of less than 1 cm. Healing is much faster than a laparotomy scar.
- Lower risk of infection: Smaller incisions mean less exposure to external contaminants.
- Less blood loss: Smaller cuts mean less damage to blood vessels and reduced bleeding. During laparoscopy, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide (CO₂), which increases intra-abdominal pressure. This compresses small blood vessels, reducing active bleeding during surgery. Laparoscopic cameras provide magnified, high-definition views of the surgical field, allowing surgeons to identify and cauterize small bleeding vessels more effectively.
❌ Cons:
- Takes longer to perform than open surgery
- Not always possible (depends on the condition)
- Requires specialized equipment and training
- Risk of injury to nearby organs (due to limited visibility)
2. Open Surgery (Traditional Surgery)
Open surgery (laparotomy) involves making a larger incision to directly access the area being operated on.
✅ Pros:
- Better visibility and access for the surgeon
- May be safer in complex cases: severe intra-abdominal infection, massive bleeding, unstable patient, large tumors or masses, bowel obstruction with severe distension, peritonitis or severe infection, late-stage pregnancy, uterine rupture, complex or prolonged surgery.
- Can be performed without special equipment
❌ Cons:
- More pain after surgery: A laparotomy requires a large incision (often several centimeters) through multiple layers: skin, fat, fascia, muscle, and peritoneum. This causes more trauma to nerves and tissues, leading to greater post-operative pain. More handling of the peritoneum (abdominal lining) in laparotomy can trigger a stronger inflammatory reaction and pain.
- Longer recovery time: Laparotomy takes weeks to months for full healing, prolonging pain. Laparoscopy heals faster (a few days to weeks) due to smaller wounds.
- Larger scar: Laparotomy has a higher risk of wound dehiscence or hematoma formation, which can promote infections.
- Higher risk of infection: In laparotomy, surgeons often handle organs directly with their hands or gauze, increasing the risk of contamination and inflammation. A large incision in laparotomy causes more tissue stress, leading to increased inflammation and a higher susceptibility to infections.
- More blood loss: Laparotomy requires more extensive dissection and tissue retraction, which can tear blood vessels and lead to more bleeding.
Which One is Better?
It depends on your condition, your health, and the surgeon’s recommendation.
In many cases, laparoscopy is preferred because of the quicker recovery, but for more complicated surgeries, open surgery may be the safer option.

