
The Importance of Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer is a significant global health issue, representing one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers among women. Effective screening and early detection are crucial in improving survival rates and outcomes for those affected. This page provides an overview of the latest guidelines for breast cancer screening and self-examination, along with pertinent world statistics.
Current Global Screening Guidelines
Health organizations around the world emphasize the importance of regular breast cancer screening. Here are the latest recommendations:
- Women Aged 20-40: An annual breast palpation by a doctor and a monthly breast self-examination are recommended.
- Women Aged 40-49: Women in this age group should discuss the benefits and risks of screening with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions about starting mammograms (every 3 years).
- Women Aged 50-69: Routine screening mammograms are recommended every two years for this group.
- Women Aged 70 and Older: Screening should continue based on individual health status and life expectancy, with a focus on personalized care.
- Self-Examination: While formal guidelines vary, many organizations advocate for regular breast self-examinations (BSE) to help women become familiar with their breast tissue.
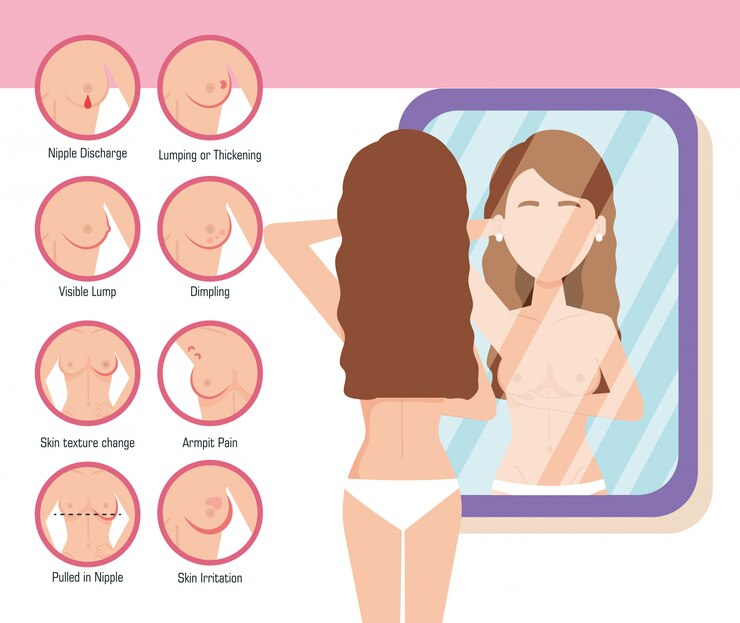
How to Perform a Breast Self-Examination (BSE)
Self-examination is a proactive measure that can help women identify changes in their breasts. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a Consistent Time: Perform your BSE monthly, ideally a few days after your menstrual period ends when breasts are least likely to be swollen or tender.
- Visual Inspection: Stand in front of a mirror and look for changes in size, shape, or skin texture. Observe both breasts for any unusual changes.
- Manual Examination: Use the pads of your fingers to feel for lumps or abnormalities. Move in a circular pattern, covering the entire breast and the area under the arms.
- Report Changes: If you notice any lumps, changes, or unusual discharge, consult a healthcare provider without delay.
Key Global Statistics
- Incidence: Breast cancer accounts for approximately 12% of all new cancer cases worldwide, with about 2.3 million women diagnosed each year.
- Mortality: It is estimated that 685,000 women die from breast cancer annually, making it the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women globally.
- Survival Rates: In high-income countries, the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer can reach up to 90%, while in low-income countries, the rate is significantly lower, highlighting disparities in access to screening and treatment.
- Awareness: Despite the importance of screening, studies indicate that only about 50% of eligible women globally participate in regular mammography screening programs.
Conclusion
Breast cancer screening and self-examination are critical elements of women’s health that can lead to early detection and better treatment outcomes. By understanding the latest guidelines and being aware of global statistics, women can take proactive steps in managing their breast health. Consult your healthcare provider to discuss personalized screening recommendations and self-examination practices. Remember, early detection can save lives!
Your health is our mission.
