Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique that allows doctors to operate with small incisions instead of large cuts. This method is commonly used for procedures in the abdomen and pelvis, offering numerous benefits to patients.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery involves making a few small incisions, typically less than 1 cm in size. Through one of these incisions, a thin tube with a tiny camera (laparoscope) is inserted. This camera provides a magnified view of the internal organs on a screen, guiding the surgeon throughout the procedure. Other small incisions allow for the insertion of specialized surgical instruments to perform the operation.
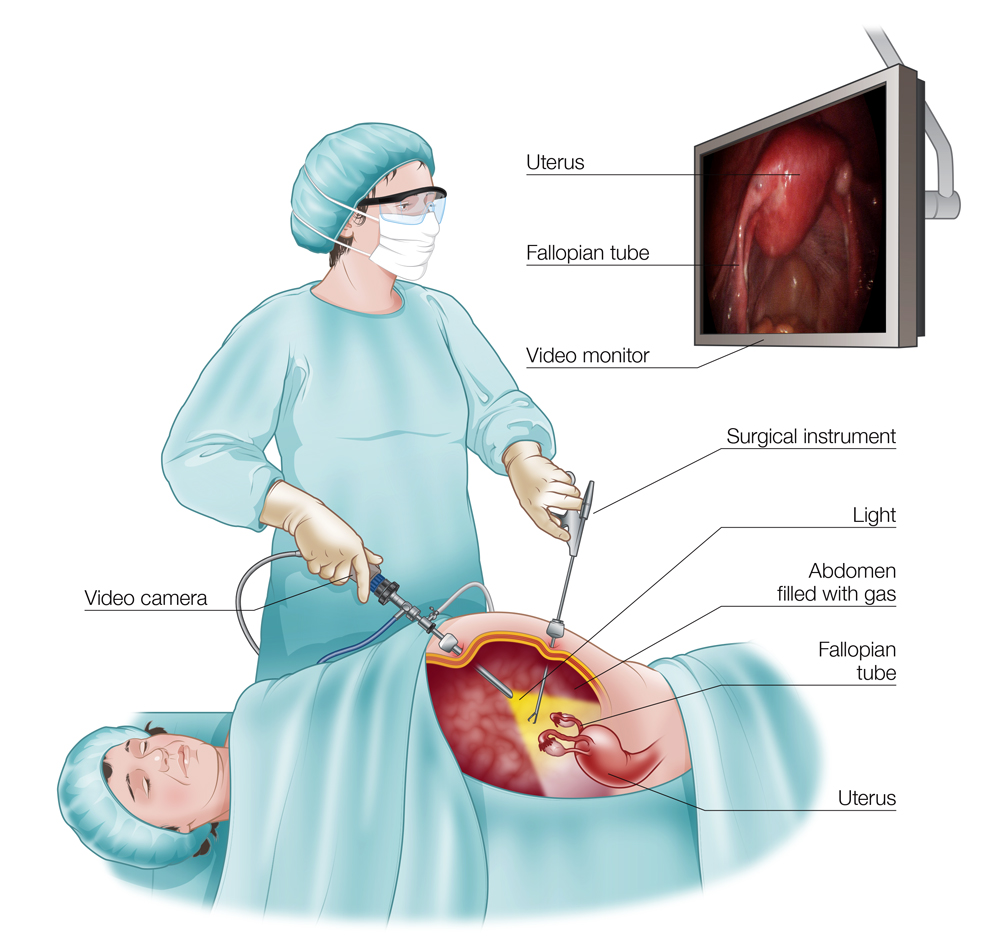
Common Procedures Using Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy is used for various surgical procedures, including:
- Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy): To treat gallstones or gallbladder disease.
- Appendectomy: To remove an inflamed appendix.
- Gynecological surgeries: Such as ovarian cyst removal, endometriosis treatment, tubal ligation or hysterectomy.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic surgery offers several advantages:
- Smaller incisions: Leading to reduced scarring.
- Less pain: Due to minimal tissue damage.
- Shorter hospital stay: Many patients can go home the same day (outpatient) or after a short stay (1-2 nights).
- Faster recovery: Most people return to normal activities sooner.
- Lower risk of infection: Smaller wounds reduce the chance of complications.
What to Expect Before, During, and After Surgery
Before Surgery
Your surgeon will explain the procedure and any necessary preparations. You will also have an anesthesia consultation. You may need blood tests or imaging studies.
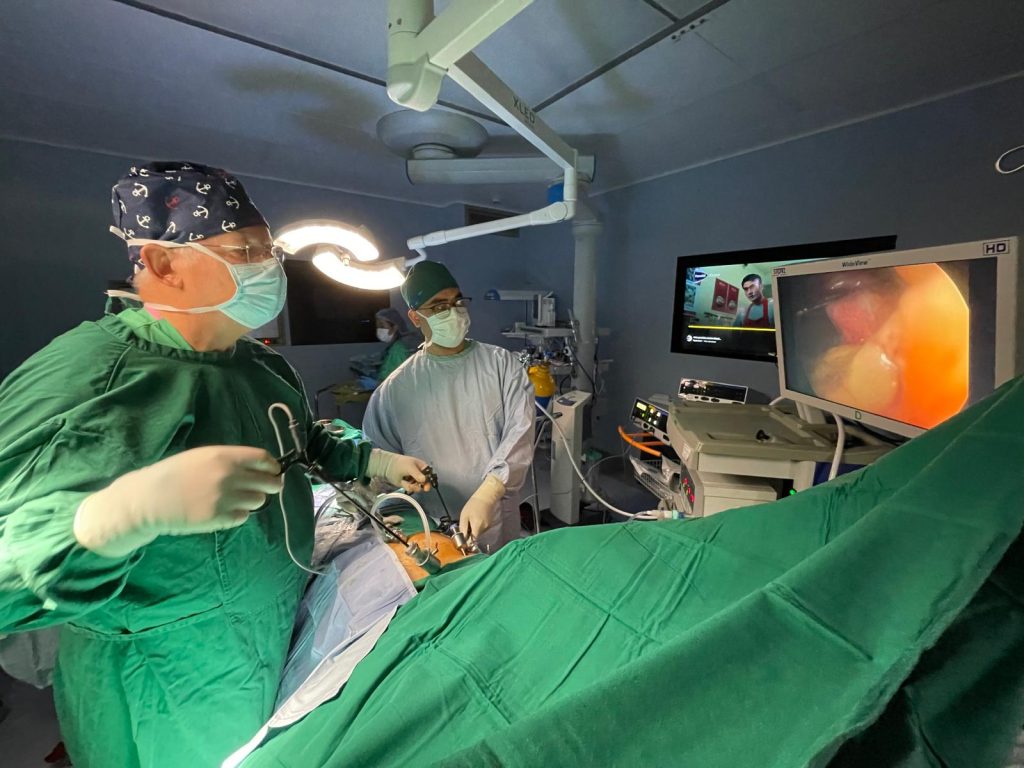
During Surgery
You will be under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep and pain-free.
Carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdomen, creating space for the surgeon to work.
The surgeon performs the procedure using the laparoscope and instruments before closing the small incisions with stitches or surgical glue.
After Surgery
You may feel mild discomfort, especially from the gas used during the procedure.
Walking and deep breathing can help relieve gas-related pain.
Recovery time varies, but many people return to normal activities within a few days.
Possible Risks and Complications
While laparoscopic surgery is generally very safe, as with any surgery, there are potential risks, such as:
- Bleeding or infection
- Injury to nearby organs
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
- Blood clots (rare but possible)
When to Seek Medical Attention
After surgery, contact your doctor if you experience:
- Severe pain that does not improve
- Fever or signs of infection (redness, swelling, or pus at incision sites)
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain Persistent nausea or vomiting
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery is a safe and effective alternative to traditional open surgery, offering quicker recovery and less discomfort. Laporoscopy is considered the gold standard for many surgeries now.
If you are considering a procedure, discuss with your doctor whether laparoscopy is the right option for you.

Your Health is our mission
